Business-type IRP (Individual Retirement Pension)
A company with under 10 people can adopt a retirement pension plan.
Under the IRP system, a company with under 10 regular employees can adopt a retirement pension plan through simplified procedures such as the omission of pension rules. Its operation structure is the same as that of the defined contribution(DC) system.
Outline
| Contribution | Over 1/12 of the employee’s annual total wage each year |
|---|---|
| Payer of contributions |
|
| Investment instruction | Employee |
| Limitation on the investment | No direct investment in stocks, ceiling on investment in risky assets |
| Level of retirement benefits | variable according to the employee’s investment results of the reserve (contribution and investment result) |
| Payment method | Lump-sum allowance or pension (pensions will be paid to a subscriber aged 55 or above, whose contribution period is 10 years or more, and the pension payment duration will be 5 years or more.) |
| Collateral loan/early settlement | Should meet legal requirements (house purchase for non-homeowners, over 6 months of medical treatment of the relevant person and his/her family, personal revival, bankruptcy, etc.) |
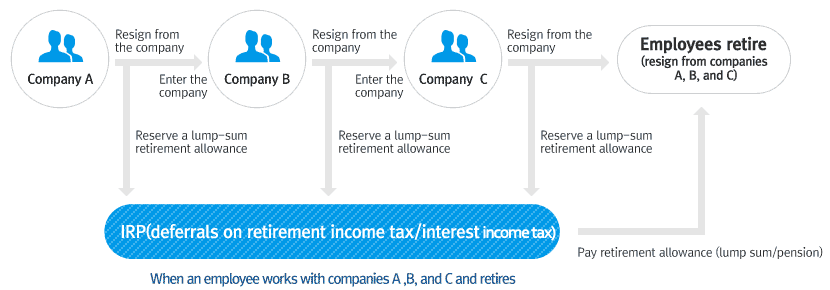
Individual Retirement Pension (IRP)
When transferring to various jobs, the employee can manage his/her received lump-sum retirement allowance without tax until he/she retires.
Under the IRP system, an employee can, when transferring to various jobs or retiring early, keep and manage his/her received retirement allowance until he/she retires.
A retired employee can transfer a lump-sum retirement allowance to IRP, obtaining deferrals on retirement income tax and increasing his/her actual received money. As such, the system is very advantageous to employees.
Due to frequent job transfers, early retirement allowance settlement, and widespread annual salary system, employees cannot efficiently utilize their lump-sum retirement benefits for their retired later lives. So, they can transfer such lump-sum retirement allowance to the IRP without incurring retirement income tax, and receive it as a lump sum or a pension after retirement.
IRP system